Pathogenesis of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis and Its Interaction with the Host

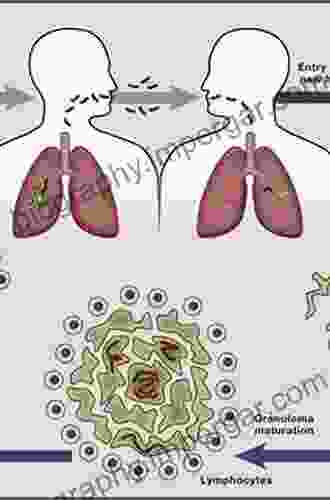
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis) is a Gram-positive, acid-fast bacterium that is the causative agent of tuberculosis (TB),a chronic infectious disease that primarily affects the lungs. TB is one of the leading causes of death from infectious diseases worldwide, with an estimated 10 million new cases and 1.5 million deaths in 2020.
The pathogenesis of M. tuberculosis is complex and involves a delicate interplay between the bacterium and the host immune system. The bacterium has evolved a number of strategies to evade the host immune response and establish a chronic infection. These strategies include:
- The ability to survive within macrophages: Macrophages are immune cells that engulf and destroy foreign particles. However, M. tuberculosis has the ability to survive within macrophages, where it can replicate and spread to other cells.
- The ability to suppress the host immune response: M. tuberculosis produces a number of factors that can suppress the host immune response, including lipoarabinomannan (LAM),which inhibits the production of cytokines that are essential for the immune response.
- The ability to form biofilms: Biofilms are communities of bacteria that are surrounded by a protective matrix of extracellular material. Biofilms can protect M. tuberculosis from the host immune response and from antibiotics.
The host immune response to M. tuberculosis is complex and involves both innate and adaptive immune mechanisms. The innate immune response is the first line of defense against infection and involves a number of mechanisms, including:
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2925 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 405 pages |
- Phagocytosis: Macrophages and neutrophils are phagocytic cells that can engulf and destroy M. tuberculosis.
- Natural killer (NK) cells: NK cells are cytotoxic lymphocytes that can kill M. tuberculosis-infected cells.
- Cytokines: Cytokines are proteins that are produced by immune cells in response to infection. Cytokines can activate other immune cells and help to coordinate the immune response.
The adaptive immune response is a more specific response to infection that is mediated by T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes. T lymphocytes are activated by antigens, which are pieces of M. tuberculosis that are recognized by the immune system. Activated T lymphocytes can kill M. tuberculosis-infected cells or produce cytokines that help to activate other immune cells. B lymphocytes produce antibodies, which are proteins that can bind to M. tuberculosis and help to neutralize it.
The pathogenesis of M. tuberculosis is determined by the balance between the host immune response and the bacterium's ability to evade the immune response and establish a chronic infection. In healthy individuals, the immune response is able to control the infection and prevent the development of disease. However, in individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or diabetes, M. tuberculosis can establish a chronic infection and cause disease.
The pathogenesis of M. tuberculosis is a complex and dynamic process that involves a delicate interplay between the bacterium and the host immune system. The bacterium has evolved a number of strategies to evade the host immune response and establish a chronic infection. However, the host immune response is able to control the infection and prevent the development of disease in healthy individuals. In individuals with weakened immune systems, M. tuberculosis can establish a chronic infection and cause disease.
Understanding the pathogenesis of M. tuberculosis is essential for the development of new and more effective treatments for TB.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2925 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 405 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Dr Hidaia Mahmood Alassouli
Dr Hidaia Mahmood Alassouli Paul Stanton Kibel
Paul Stanton Kibel Stephanie Cronin
Stephanie Cronin Paul Wanke
Paul Wanke Irene C Mammarella
Irene C Mammarella Gianfranco Cariolaro
Gianfranco Cariolaro Marion Dolan
Marion Dolan Diane Warner
Diane Warner Raju L Bhardwaj
Raju L Bhardwaj Mark Arsenault
Mark Arsenault Paul Stanley
Paul Stanley Andrew Klavan
Andrew Klavan Michael Black
Michael Black Lloyd L Lee
Lloyd L Lee Michael Sudduth
Michael Sudduth John Ross Bowie
John Ross Bowie Agatha Christie
Agatha Christie Joseph H Di Leo
Joseph H Di Leo Asher Susser
Asher Susser Matthew Moss
Matthew Moss
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Camden MitchellCarnap's Ideal of Explication and Naturalism: A Cornerstone of Analytic...
Camden MitchellCarnap's Ideal of Explication and Naturalism: A Cornerstone of Analytic...
 Hamilton BellDetective Galileo: The Mind-Bending Mystery Novel That Will Keep You Guessing
Hamilton BellDetective Galileo: The Mind-Bending Mystery Novel That Will Keep You Guessing
 Charlie ScottThe Fundamentals of Estate Planning Maryland Second Edition: Securing Your...
Charlie ScottThe Fundamentals of Estate Planning Maryland Second Edition: Securing Your... Dwight BlairFollow ·4.5k
Dwight BlairFollow ·4.5k Todd TurnerFollow ·4.3k
Todd TurnerFollow ·4.3k Edmund HayesFollow ·5.7k
Edmund HayesFollow ·5.7k Dean ButlerFollow ·7k
Dean ButlerFollow ·7k Jacob HayesFollow ·15.5k
Jacob HayesFollow ·15.5k Hector BlairFollow ·6.4k
Hector BlairFollow ·6.4k Neal WardFollow ·16.4k
Neal WardFollow ·16.4k Douglas FosterFollow ·9.5k
Douglas FosterFollow ·9.5k

 Jeff Foster
Jeff FosterExploring Culture: Exercises, Stories, and Synthetic...
Culture is a complex and multifaceted...

 Eddie Bell
Eddie BellPrinciples of ICD-10 Coding Workbook: Your Comprehensive...
Empower Yourself with the...

 Nikolai Gogol
Nikolai GogolOttoman Egypt: A Catalyst for the Modern World's...
: A Hidden Gem in...

 Jorge Amado
Jorge AmadoUnveiling the Secrets of Group Intervention: A...
In the realm of...

 Dakota Powell
Dakota PowellUnveiling the Interwoven Nature of Animality and Colonial...
Welcome to an...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2925 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 405 pages |