Regulatory Cells and Clinical Application: A Comprehensive Guide

In the ever-evolving landscape of modern medicine, the field of regulatory cells has emerged as a beacon of hope in the pursuit of novel and effective therapeutic strategies. This comprehensive guide will delve into the fascinating world of regulatory cells, shedding light on their intricate functions, clinical applications, and the potential they hold for transforming healthcare.
Understanding Regulatory Cells
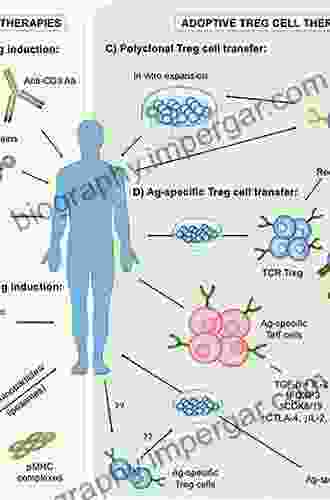
Regulatory cells are a specialized group of immune cells that play a crucial role in maintaining immune homeostasis and preventing excessive immune responses. These cells suppress or dampen the activity of other immune cells, ensuring that the immune system responds appropriately to foreign invaders without harming healthy tissues. Regulatory cells include various subsets, such as regulatory T cells (Tregs),regulatory B cells (Bregs),and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs).
4.8 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2915 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 1093 pages |
Mechanism of Action
Regulatory cells employ a diverse array of mechanisms to suppress immune responses. Tregs, for instance, release immunosuppressive cytokines like interleukin-10 (IL-10) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta),which inhibit the proliferation and activation of other immune cells. Bregs can produce antibodies that neutralize inflammatory cytokines or bind to immune cell receptors, blocking their activation. MDSCs, on the other hand, can inhibit T cell responses through the production of reactive oxygen species or by expressing immune checkpoint proteins.
Clinical Applications
The therapeutic potential of regulatory cells has sparked immense interest in the field of clinical medicine. Researchers and clinicians are exploring the use of regulatory cells in a variety of disease settings, including:
- Autoimmune diseases: Regulatory cells can be harnessed to suppress excessive immune responses in autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and lupus.
- Allergic disFree Downloads: Regulatory cells can modulate immune responses in allergic diseases like asthma and hay fever, reducing inflammation and alleviating symptoms.
- Organ transplantation: Regulatory cells can prevent the rejection of transplanted organs by suppressing immune responses against foreign tissue.
- Cancer immunotherapy: Regulatory cells can be manipulated to enhance anti-tumor immune responses, improving the efficacy of cancer treatments.
Research Breakthroughs and Future Directions
The field of regulatory cells is rapidly advancing, with ongoing research unlocking new insights and expanding their therapeutic potential. Some recent breakthroughs and promising future directions include:
- Identification of new regulatory cell subsets: Researchers are discovering new subsets of regulatory cells with distinct functions and therapeutic implications.
- Enhanced understanding of regulatory cell dynamics: Studies are elucidating how regulatory cells interact with other immune cells and adapt to different disease environments.
- Development of novel therapeutic approaches: Clinical trials are evaluating strategies to expand or enhance the function of regulatory cells for various diseases.
- Personalized medicine: Researchers are exploring ways to tailor regulatory cell-based therapies to individual patient profiles, maximizing therapeutic efficacy.
Regulatory cells represent a promising frontier in modern medicine, offering a unique approach to treating a wide range of diseases. As research continues to unravel their intricate functions and clinical applications, regulatory cell-based therapies have the potential to revolutionize healthcare by restoring immune balance and promoting tissue healing. This comprehensive guide provides a valuable resource for healthcare professionals, scientists, and anyone interested in the transformative potential of regulatory cells.
4.8 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2915 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 1093 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia A S Park
A S Park Alain Badiou
Alain Badiou Alexander Todorov
Alexander Todorov Megapode Books
Megapode Books Helen Kleberg Groves
Helen Kleberg Groves Lillian Bradley
Lillian Bradley James Gleeson
James Gleeson Philip Ashton Rollins
Philip Ashton Rollins Debra L Kalmanowitz
Debra L Kalmanowitz Jonn Elledge
Jonn Elledge Gerald Rogers
Gerald Rogers Cathy Glass
Cathy Glass Deborah Willis
Deborah Willis Richard F Hirsh
Richard F Hirsh Melusine Draco
Melusine Draco Federico Pasini
Federico Pasini Linda Gromko Md
Linda Gromko Md Mark Jerome Walters
Mark Jerome Walters J H Reyner
J H Reyner Christa Davis Acampora
Christa Davis Acampora
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Dashawn HayesFoucault, The Family, and Politics: Unveiling the Power Dynamics Within the...
Dashawn HayesFoucault, The Family, and Politics: Unveiling the Power Dynamics Within the... Jarrett BlairFollow ·16.2k
Jarrett BlairFollow ·16.2k Denzel HayesFollow ·3.2k
Denzel HayesFollow ·3.2k J.R.R. TolkienFollow ·10k
J.R.R. TolkienFollow ·10k Beau CarterFollow ·15.2k
Beau CarterFollow ·15.2k Jules VerneFollow ·15.5k
Jules VerneFollow ·15.5k Brody PowellFollow ·9.5k
Brody PowellFollow ·9.5k Fyodor DostoevskyFollow ·12.9k
Fyodor DostoevskyFollow ·12.9k Hank MitchellFollow ·3.8k
Hank MitchellFollow ·3.8k

 Jeff Foster
Jeff FosterExploring Culture: Exercises, Stories, and Synthetic...
Culture is a complex and multifaceted...

 Eddie Bell
Eddie BellPrinciples of ICD-10 Coding Workbook: Your Comprehensive...
Empower Yourself with the...

 Nikolai Gogol
Nikolai GogolOttoman Egypt: A Catalyst for the Modern World's...
: A Hidden Gem in...

 Jorge Amado
Jorge AmadoUnveiling the Secrets of Group Intervention: A...
In the realm of...

 Dakota Powell
Dakota PowellUnveiling the Interwoven Nature of Animality and Colonial...
Welcome to an...
4.8 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2915 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 1093 pages |